Emergency Cases
+91 99686 35204
Opening Hours
Monday to Saturday
09:00 am – 10.00 pm
Sunday
09:00 am – 5.00 pm
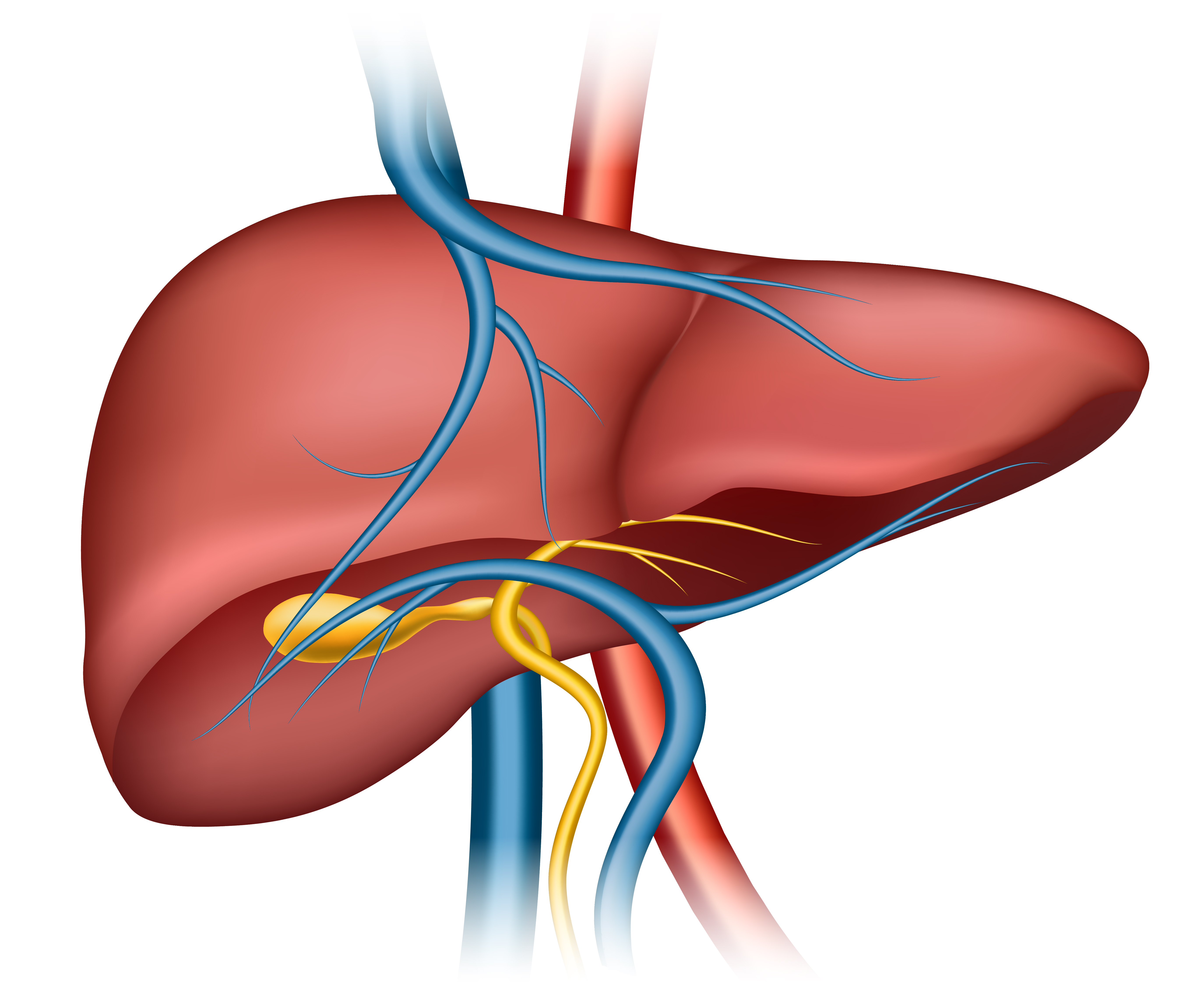
Liver Biopsy
A liver biopsy is a medical procedure that involves taking a small sample of liver tissue for analysis. The procedure is usually performed by a doctor in a hospital or clinic and involves using a needle to remove the tissue from the liver.
Why is Liver Biopsy Done?
A liver biopsy may be done to diagnose certain liver conditions such as:
- Liver Fibrosis or Cirrhosis: Liver fibrosis is a condition where the liver develops scar tissue, which can lead to liver cirrhosis if not treated. A biopsy can help to determine the severity of the fibrosis and cirrhosis.
- Liver Cancer: Liver biopsy can help to diagnose liver cancer or other types of liver tumors.
- Hepatitis: A biopsy can help to diagnose the type and severity of hepatitis, which is an inflammation of the liver.
- Other Liver Diseases: Biopsy may be done to diagnose other liver diseases such as fatty liver disease, autoimmune hepatitis, or hemochromatosis.
How is Liver Biopsy Done?
A liver biopsy is usually done on an outpatient basis and takes about 30 minutes to an hour to complete. Before the procedure, the patient may be given medication to help them relax and to numb the area where the biopsy will be taken.
During the procedure, the patient lies on their back with their right arm raised above their head. The doctor locates the liver using ultrasound or a similar imaging technique and then inserts a thin needle through the skin and into the liver. The needle is then used to remove a small sample of liver tissue.
After the biopsy, the patient is monitored for a short period of time to ensure that there are no complications. The patient may be advised to avoid certain activities, such as heavy lifting, for a few days after the procedure.
Risks and Complications
While a liver biopsy is generally considered a safe procedure, there are some risks and potential complications. These may include:
- Pain or Discomfort: Some patients may experience pain or discomfort at the site of the biopsy for a few days after the procedure.
- Bleeding: There is a small risk of bleeding from the site of the biopsy, especially if the patient has a bleeding disorder or takes blood-thinning medications.
- Infection: There is a small risk of infection at the site of the biopsy or in the liver.
- Pneumothorax: In rare cases, the needle used for the biopsy may accidentally puncture the lung, causing air to leak into the chest cavity.
- Other complications: Rarely, other complications may occur such as bile leakage, damage to nearby organs, or an allergic reaction to the anesthesia or medication used during the procedure.
Preparing for a Liver Biopsy
Before the procedure, the patient will usually have a medical evaluation to determine if they are a good candidate for a liver biopsy. This may include blood tests, imaging tests, and a physical examination.
The patient may also need to stop taking certain medications before the biopsy, such as blood thinners or aspirin, to reduce the risk of bleeding. The doctor may also advise the patient to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours before the biopsy.
After the biopsy, the patient may be advised to rest for a short period of time and to avoid certain activities for a few days. The doctor will typically schedule a follow-up appointment to discuss the results of the biopsy and any necessary treatment.
Conclusion
Liver biopsy is a valuable diagnostic tool for liver diseases such as fibrosis, cirrhosis, cancer, and hepatitis. While the procedure carries some risks and potential complications, it is generally considered safe and effective. If you are experiencing symptoms of liver disease or have risk factors for liver disease, talk to your doctor about whether a liver biopsy is right for you.